LCA - Lowest Common Ancestor
no tags
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one simple path. In other words, any connected graph without cycles is a tree. - Wikipedia
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) is a concept in graph theory and computer science. Let T be a rooted tree with N nodes. The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself). - Wikipedia
Your task in this problem is to find the LCA of any two given nodes v and w in a given tree T.
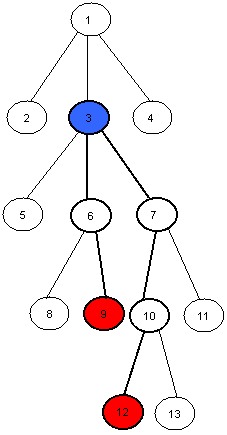
For example the LCA of nodes 9 and 12 in this tree is the node number 3.
Input
The first line of input will be the number of test cases. Each test case will start with a number N the number of nodes in the tree, 1 <= N <= 1,000. Nodes are numbered from 1 to N. The next N lines each one will start with a number M the number of child nodes of the Nth node, 0 <= M <= 999 followed by M numbers the child nodes of the Nth node. The next line will be a number Q the number of queries you have to answer for the given tree T, 1 <= Q <= 1000. The next Q lines each one will have two number v and w in which you have to find the LCA of v and w in T, 1 <= v, w <= 1,000.
Input will guarantee that there is only one root and no cycles.
Output
For each test case print Q + 1 lines, The first line will have “Case C:” without quotes where C is the case number starting with 1. The next Q lines should be the LCA of the given v and w respectively.
Example
Input:
1
7
3 2 3 4
0
3 5 6 7
0
0
0
0
2
5 7
2 7
Output:
Case 1: 3 1
// node of the tree is 1 based index so if in any problem nodes are
// 0 based than make it 1 based by increasein 1 each node while
// makin graph , also at the time of query increase by 1
// all array euler[1000000],level[1000000],f_occ[1000000] are 0 based index
// seg tree is 1 based index .....
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int lli;
int euler[1000000],level[1000000],f_occ[1000000];
int id=0;
list<int > li[1000000];
int kk=0;
lli dist[1000000];
#define inf 100000000
struct st
{
int val;
int index;
} tree[1000000];
void dfs(int start,int lev,int par)
{
euler[id]=start;
level[id]=lev;
f_occ[start]=min(f_occ[start],id);
id++;
list<int>:: iterator it;
for(it=li[start].begin();it!=li[start].end();it++)
{
if(*it!=par)
{
dfs(*it,lev+1,start);
euler[id]=start;
level[id]=lev;
f_occ[start]=min(f_occ[start],id);
id++;
}
}
}
st query(int node,int start,int end,int r1,int r2)
{
if(start>end || r1>end || r2<start)
{
st ab;
ab.val=inf;
ab.index=-1;
return ab;
}
if(r1<=start && r2>=end)
{
return tree[node];
}
else
{
st q1=query(2*node,start,(start+end)/2,r1,r2);
st q2=query(2*node+1,((start+end)/2)+1,end,r1,r2);
if(q1.val<q2.val) return q1;
else return q2;
}
}
void build(int node , int start,int end)
{
if(start==end)
{
tree[node].val=level[start];
tree[node].index=start;
return ;
}
else if(start>end)
{
tree[node].val=inf;
tree[node].index=-1;
return ;
}
else
{
build(2*node,start,(start+end)/2);
build(2*node+1,((start+end)/2)+1,end);
if(tree[2*node].val<tree[2*node+1].val)
{
tree[node].val=tree[2*node].val;
tree[node].index=tree[2*node].index;
}
else
{
tree[node].val=tree[2*node+1].val;
tree[node].index=tree[2*node+1].index;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
int cc=0;
while(t--)
{
cout<<"Case "<<++cc<<":"<<endl;
int n;
cin>>n;
id=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
li[i].clear();
int k;
cin>>k;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
li[i].push_back(x);
li[x].push_back(i);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<=2*n;i++) f_occ[i]=1000000;
dfs(1,1,0);
id--;
build(1,0,id);
int q;
cin>>q;
while(q--)
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
int x1=f_occ[a];
int x2=f_occ[b];
if(x1>x2) swap(x1,x2);
st lc=query(1,0,id,x1,x2);
int lca=euler[lc.index];
cout<<lca<<endl;
}
}
}
---------------------------------------------binary rais solution------------------------------------
// tree is treated as 1 based
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int lli;
list<int>li[1010];
lli dp[1010][30];
int lev[1010];
int dfs(int start,int par,int le)
{
lev[start]=le;
list<int>:: iterator it;
for(it=li[start].begin();it!=li[start].end();it++)
{
if(*it!=par)
{
dp[*it][0]=start;
lev[*it]=le+1;
dfs(*it,start,le+1);
}
}
}
int binary_rais(int a,int b)// return lca of a,b
{
// cout<<" find par of "<<a<<"level a "<<lev[a]<<b<<" lev b "<<lev[b]<<endl;
if(lev[a]<lev[b]) swap(a,b);
int lg;
/// maximum jump that can be alloweable to make both a and
// b at same level
for(lg=1;(1<<lg)<=lev[a];lg++);
lg--;
// this will make both at same level
for(int i=lg;i>=0;i--)
{
if(lev[a]-(1<<i)>=lev[b])
{
a=dp[a][i];
}
}
// cout<<" at same level "<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;
if(a==b) return a;
else
{
for(int i=lg;i>=0;i--)
{
if(dp[a][i]!=-1 && dp[a][i]!=dp[b][i])
{
a=dp[a][i];
b=dp[b][i];
}
}
return dp[a][0];
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
int cas=1;
while(t--)
{
cout<<"Case "<<cas++<<":"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<1010;i++)li[i].clear();
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int k; cin>>k;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++)
{
int a;
cin>>a;
li[i].push_back(a);
}
}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
dp[1][0]=0;
dfs(1,-1,1);
int max_h=20;
// maximum height
for(int i=1;i<=max_h;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(dp[j][i-1]!=-1)
dp[j][i]=dp[dp[j][i-1]][i-1];//
}
}
int q;
cin>>q;
while(q--)
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<< binary_rais(a,b)<<endl;
}
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment